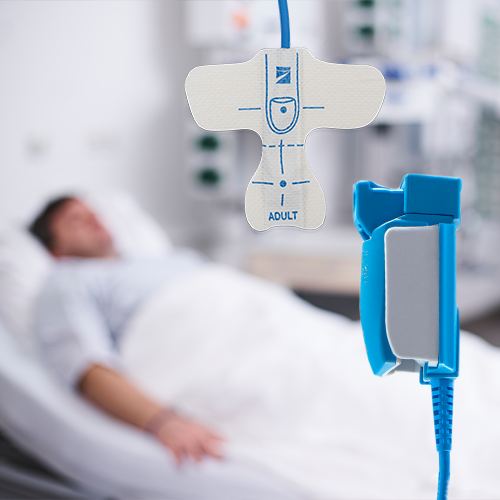
SpO2 Sensors

Overview
The Pulse Oximeter is a device that continuously and non-invasively monitors the level of oxygen in the patients’ bloodstream. The principle of Pulse oximetry was invented by Dr. Takuo Aoyagi, an engineer at Nihon Kohden, in 1972. Nihon Kohden has two types of SpO2 probes: Single patient use probes and reusable probes. Select an appropriate type according to your application.

Single-patient use sensors
- For long-term monitoring, the structure is designed to prevent compression and misalignment
- A one-piece probe with adhesive tape that is easy to attach to the patient skin
- Easy to apply with full-range of sizes, from neonate to adult
Reusable sensors
- Ideal for spot monitoring
- A unique design to offer painless and supreme comfort to the patient by providing an optimal distribution of pressure which prevents blood clots or skin trauma
- Cleaning and disinfection are available
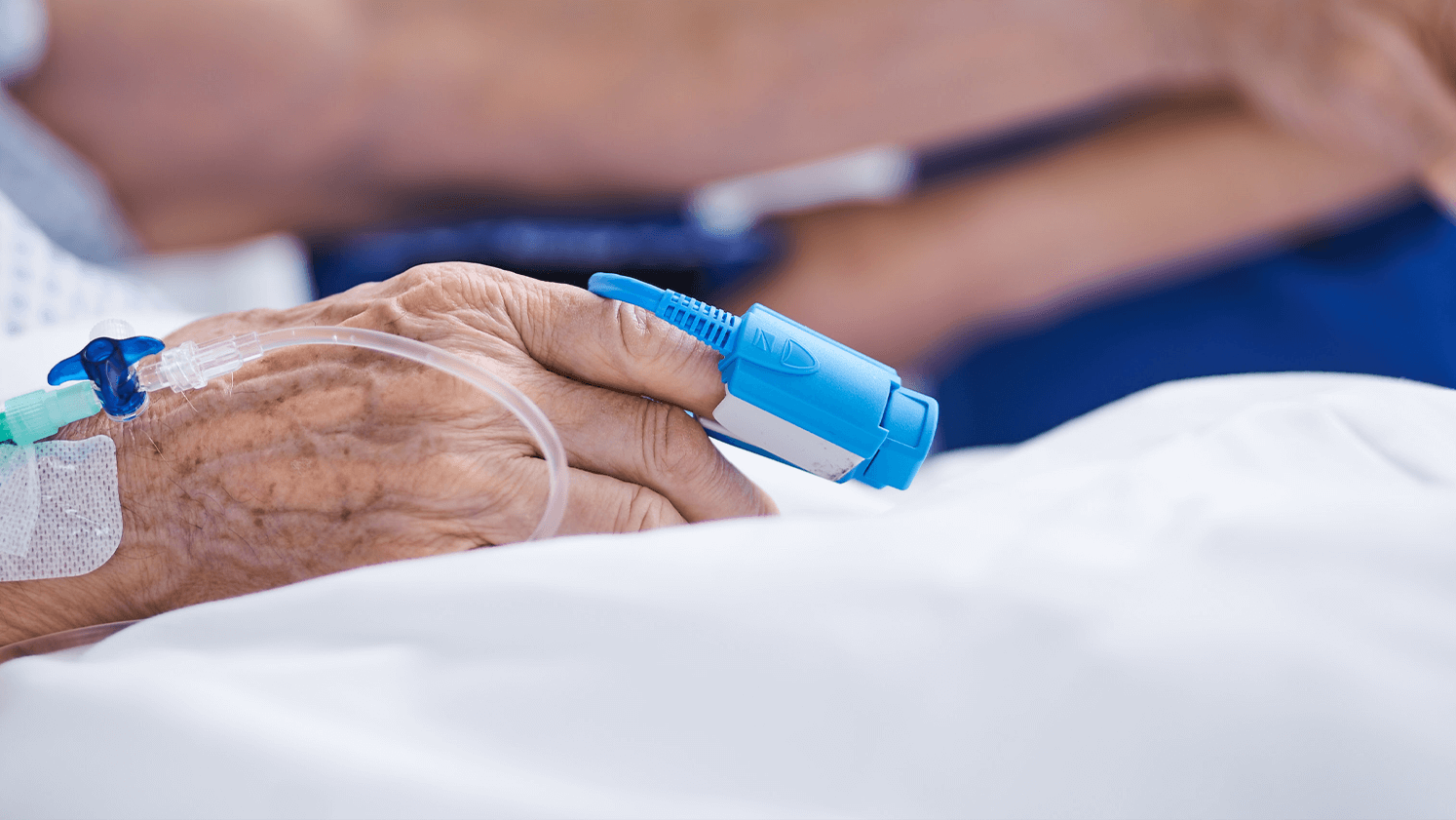
For better SpO2 Monitoring
The SpO2 value is often affected by the patient’s condition, artifacts created by external devices or by inappropriate attachment of probes. Nihon Kohden’s monitor has several features for better SpO2 measurement. Let us introduce four features: Signal Quality Index (SQI), Pulse-amplitude Index (PI), Response, and Sensitivity Mode.^
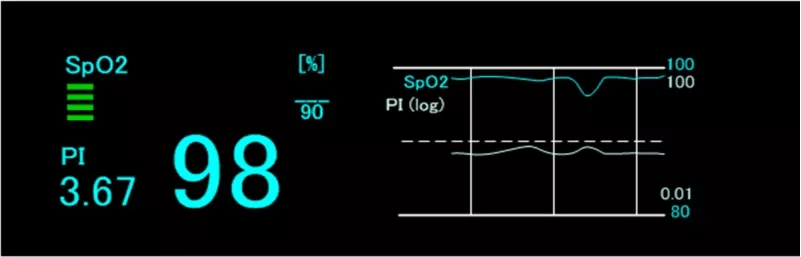
Signal Quality Index (SQI)
Nihon Kohden’s monitors display the quality of the pulse waveform signal, which is used to measure SpO2, by a bar graph. If the SQI bar graph displays 2 yellow bars or below, check for the patient’s physical movement and/or how the probe is attached.
| SQI Bar Graph | Signal Quality |
|---|---|
| Good. | |
| There may be some artifacts. | |
| There may be significant artifacts. If this continues for a while, check the patient and probe attachment site. | |
| Very low. Check the patient and probe attachment site. | |
| The signal cannot be detected. |
Pulse-amplitude Index (PI)
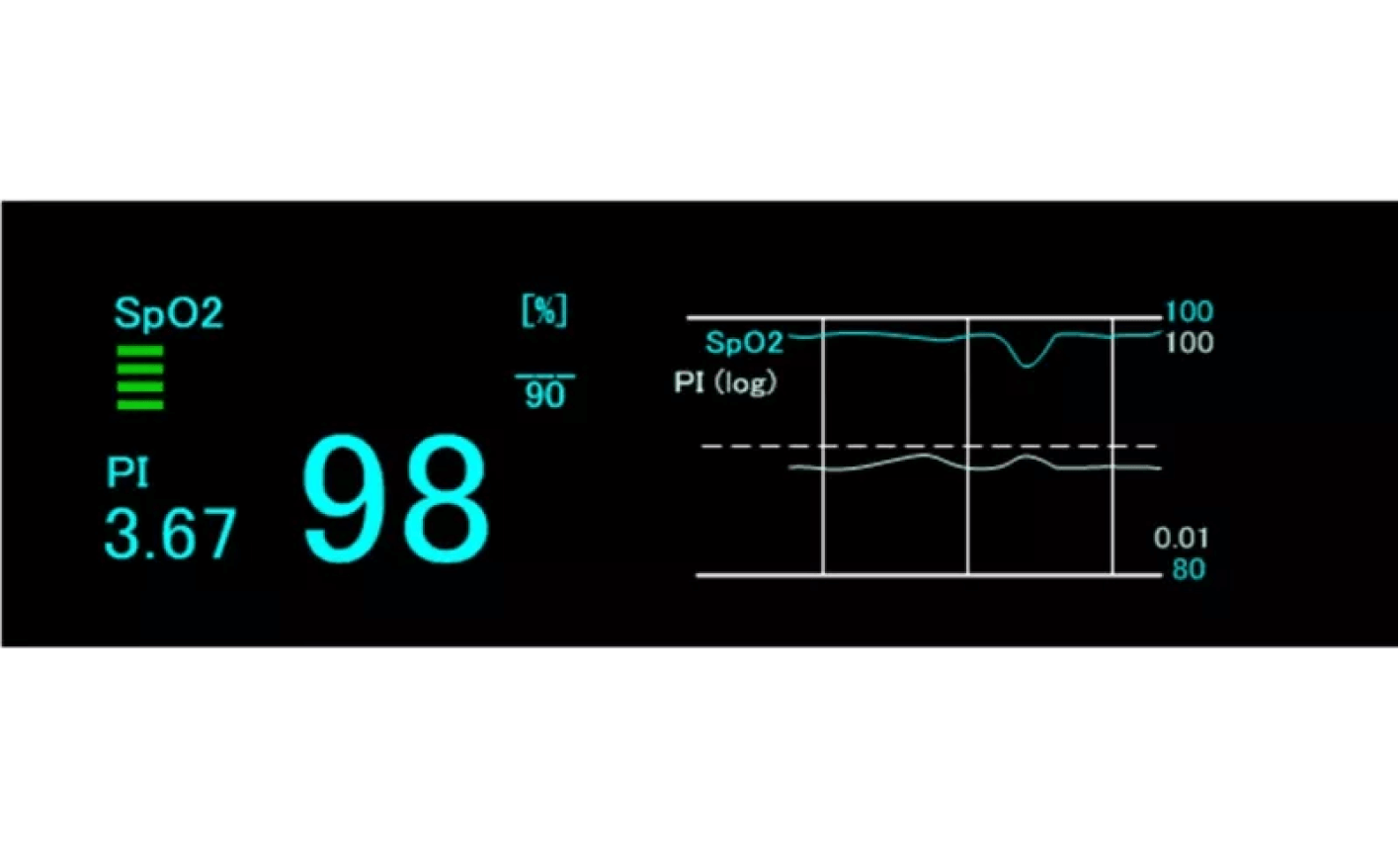
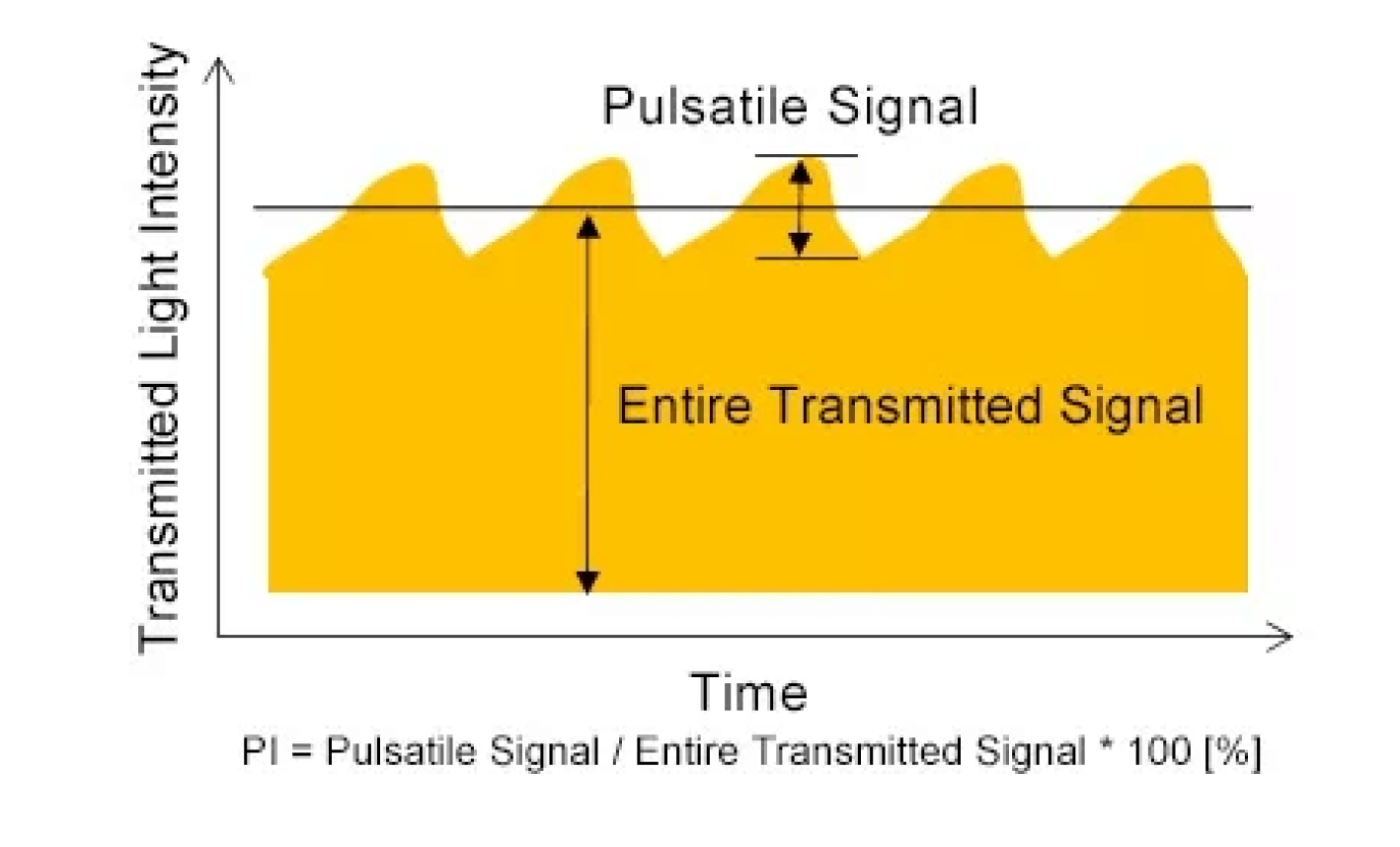
The Pulse-amplitude Index, PI, indicates the percentage of the pulsatile signal as a proportion of the entire transmitted infrared signal. It fluctuates depending on the size of transmitted signal and the size of the pulsatile signal obtained from the probe attached to the patient.
PI can be used as an index to confirm the circulation of the attachment site as well as to check the condition of an attachment site of SpO2 probe so if the attachment site is too thick or if an SpO2 probe is inappropriately attached, the intensity of the transmitted light decreases, meaning the PI value becomes low. When the PI is low, any of the following situations might be happening.
- Measurement site is cold
- SpO2 probe is attached too tight
- The patient is in a condition of shock
- The patient is a premature baby
If the PI value is low, check the probe attachment as the probe may block blood flow of the measurement site due to the high pressure if it is attached too tight. If the PI value is low, but the probe is properly attached, change the probe attachment site for more reliable SpO2 measurement. If the SpO2 value and PI value are dropping simultaneously, there is a possibility that the SpO2 probe might have deviated from the correct attachment position.
Response: Fast, Normal, Slow
This is a feature that lets you set the response times of the SpO2;value. We have Normal, Slow and Fast mode.
Normal: Standard response time
Slow: Slower response. This is useful when you want to control transient fluctuations in the SpO2;value.
Fast: Faster response. This can be used in a situation that requires an extremely fast response.
When measurement condition is unstable such as due to strenuous movement of the patient, response may become slower in all modes.

Sensitivity Mode
Sensitivity mode allows you to improve the sensitivity of the pulse wave, therefore this feature is useful when it is difficult to detect the pulse of a patient with peripheral circulation insufficiency or when an IABP (Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump) is used. On the other hand, an SpO2 value may be measured even if the probe is detached from the patient. Therefore, when selecting “Max” for the setting, it is necessary to confirm that the probe is appropriately attached to the patient.


Tips for accurate measurement
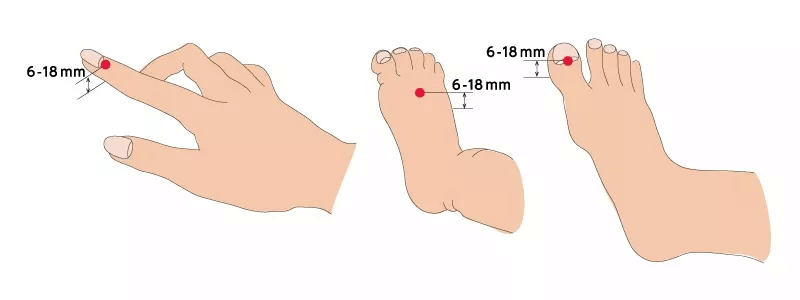
1. Select an attachment site with an appropriate thickness
A pulse oximeter detects the light that penetrates the measurement site. In most cases, a probe should be attached across a measurement site with a thickness of 6-18 mm to obtain stable and accurate SpO2;value.
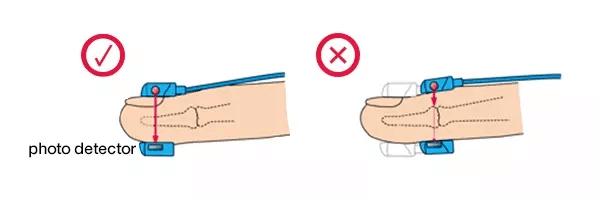
2. Attach the sensor correctly
To obtain stable and accurate SpO2 measurement, the probes should be attached in the correct position so that the light emitter and the photo detector face each other like in the following image.
3. Periodically change the attachment site
To prevent skin damage due to prolonged attachment, it is important to check and change the attachment site if necessary.
For single-patient use probes: within every 8 hours
For reusable types: within every 4 hours