
iNIBP

What is iNIBP?
iNIBP is Nihon Kohden's non-invasive blood pressure measurement algorithm using inflation technology. iNIBP completes the measurement while inflating a cuff. The iNIBP measurement time is shorter and target inflation pressure is lower as compared to the conventional method, thus, speedy and gentle measurement gives less stress to both patients and caregivers.
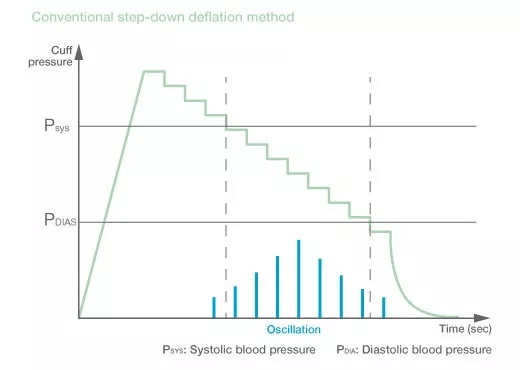
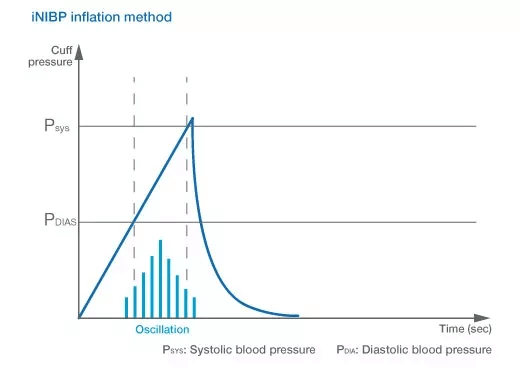
Advantages of iNIBP
The advantages of iNIBP are best demonstrated when patient's blood pressure is varying, for example during surgery. As iNIBP inflates while sensing blood pressure variation, it can complete the measurement in a shorter amount of time without applying excessive and unnecessary pressure to the patient.
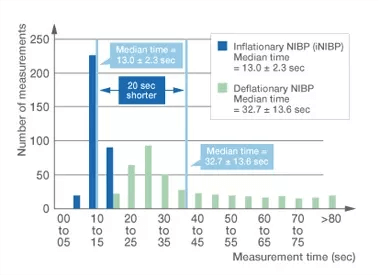
Histogram of measurement time of iNIBP inflation method and deflation method
323 measurement data collected in 64 cases in the operating room were used to compare measurement time of iNIBP inflation method and conventional deflation method. With the iNIBP technology from Nihon Kohden, the algorithm affects a slow inflation of a cuff while simultaneously detecting oscillations, then deflates the cuff as soon as systolic blood pressure (SYS) is determined.
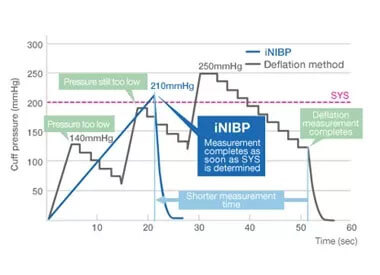
Measurement simulation: SYS elevated to 200 mmHg
iNIBP can complete the measurement in a shorter amount of time as it inflates the cuff while sensing blood pressure variation and detecting oscillations, whereas the deflation method needs to repeat the inflation-deflation cycle when the target inflation pressure based on previous systolic pressure measurements are comparatively low.
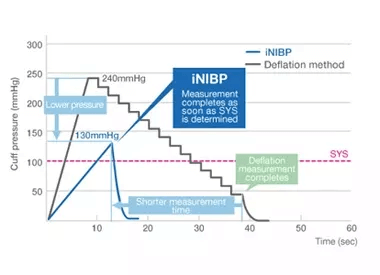
Measurement simulation: SYS dropped to 100 mmHg from 200 mmHg
iNIBP inflates the cuff to only slightly above the SYS while detecting oscillations and completes the measurement in a shorter amount of time, in comparison with the deflation method which inflates a cuff based on a pre-determined target pressure that often significantly exceeds actual SYS, leading to longer measurement times with the increased potential for patient discomfort.
Material Downloads - iNIBP
-
Comparison of iNIBP and conventional deflation in detecting hypotension during Caesarean section
-
Comparison of iNIBP inflation method and conventional deflation method in hemodialysis patients.
-
iNIBP Case Report - Experiences in OR
-
Usefulness of Linear Inflation Method NIBP (iNIBP) during Induction of Anesthesia