

synECi18

Qu’est-ce qu’un ECG synthétisé?
L’examen ECG le plus courant est l’ECG standard à 12 dérivations. Il est simple à mesurer, a une faible charge pour le corps et observer le cœur sous ces 12 directions fournit beaucoup d’informations avec une large gamme d’applications cliniques. Cependant, certaines zones, en particulier les changements pathologiques dans le ventricule droit et la paroi postérieure, ne peuvent pas être observées avec l’ECG à 12 dérivations.
L’ECG synthétisé à 18 dérivations utilise les formes d’onde de l’ECG à 12 dérivations pour dériver mathématiquement les formes d’onde des dérivations thoraciques droites (V3R, V4R, V5R) et des dérivations dorsales (V7, V8, V9). La procédure de mesure est la même que celle de l’ECG standard à 12 dérivations, mais plus d’informations peuvent être obtenues. L’ECG synthétisé à 18 dérivations est censé être utile pour détecter les infarctus du côté droit et postérieurs.
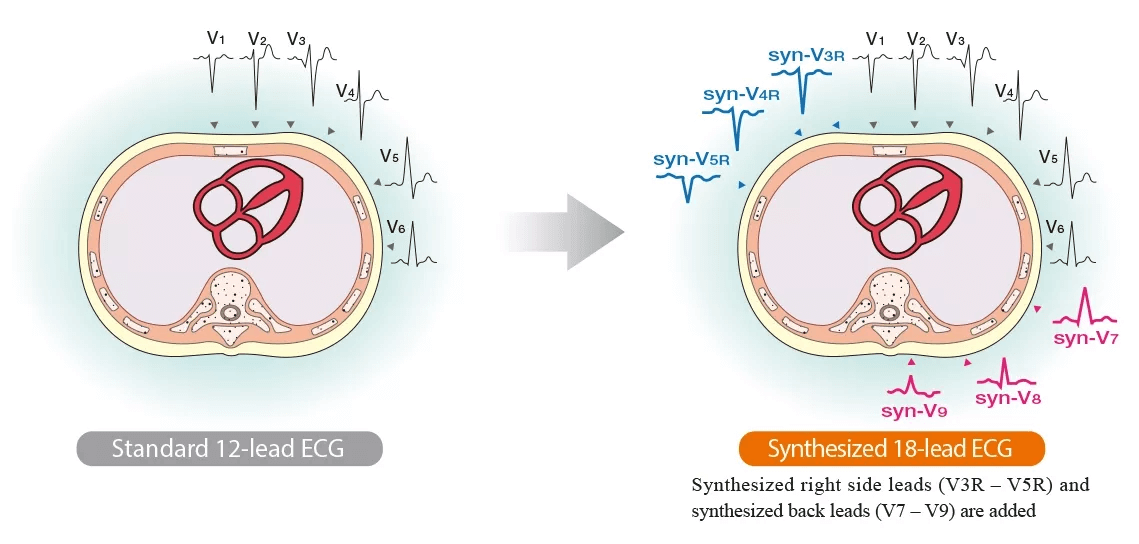
Principe des formes d’onde synthétisées
Les vecteurs cardioélectriques instantanés sont mesurés en continu à partir des données standard de l’ECG à 12 dérivations, et l’ECG pour les dérivations droites (V3R, V4R et V5R) et les dérivations dorsales (V7, V8 et V9) est synthétisé à partir de ces données.
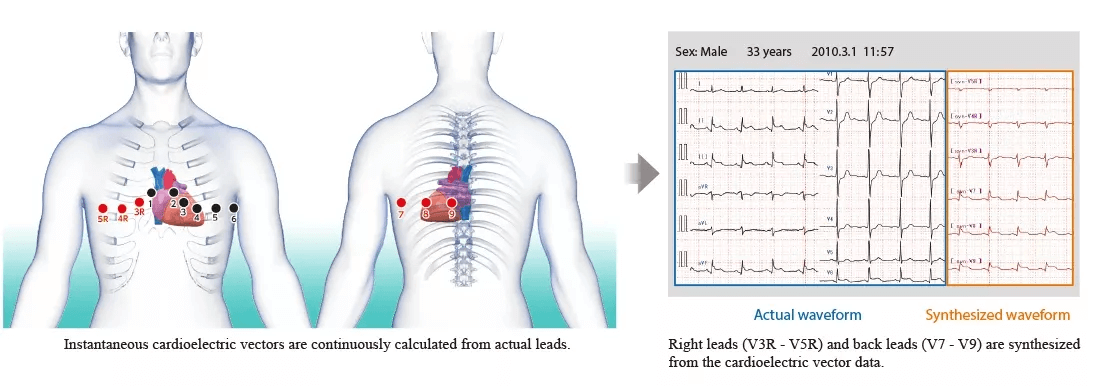
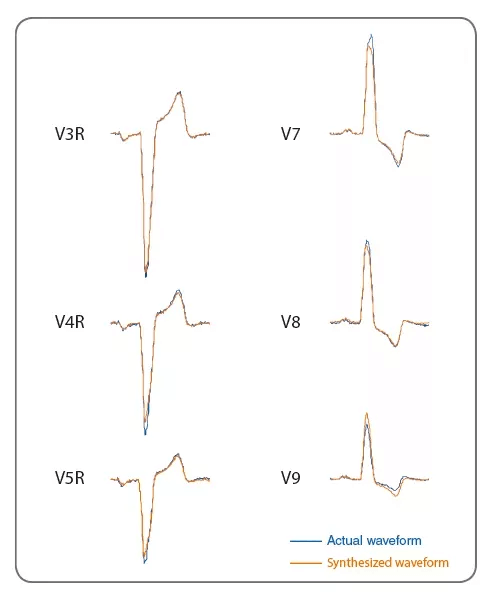
L’exemple de gauche montre des formes d’onde réellement mesurées et des formes d’onde synthétisées. D’autres données présentent également une bonne corrélation avec l’ECG réellement mesuré. Cela suggère que nous pouvons obtenir des informations utiles correspondant à l’état du cœur.
Références
1. US Patent No. : US8.005.532: Electrocardiograph with extended function, and extended lead electrocardiogram deriving method.Inventor: DamingWei. ph. D
2. Wei D., et al.: Derived electrocardiograms on the posterior leads from 12-lead system: method and evaluation.Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of IEEE IEMBS 2003; 1: 74-77.
3. KatohT., et al., Clinical Significance of Synthesized Posterior Right-Sided Chest Lead Electrocardiograms in Patients with Acute Chest Pain. J Nippon Med Sch 2011: 78 (1): 22-29.
4. Kenichi Harumi. Guide for electrocardiographic diagnosis. Sogo Rinsho. extra number. 1995.
5. WlliottM Antman. MD. FACC. FAHA. Chalret al. ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2004:110:e82-e292.
6. The 73thAnnual Scientific Meeting of the Japanese Circulation Society, March 20-22, 2009Diagnostic Improvement for Detecting Posterior Myocardial Infarction Using Lead V9 on Surface ECG: Comparison with Echocardiography.Nobuhiko Haruki*, Hidetoshi Yoshitani*, Hiromi Nakai*, Kyoko Otani*, Kyoko Kaku*, Toshiyuki Ota*, Yutaka Otsuji*
7. International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrocardiology(ISHNE)2009June 4-62009YokohamaDiagnostic Improvement for Detecting Posterior Myocardial Infarction Using Virtual ECG: Comparison with Echocardiography.Nobuhiko Haruki*1, Masaki Takeuchi*1, Hiromi Nakai*1, Kyoko Kaku*1, Hidetoshi Yoshitani*1, Jiro Suto*2, Yutaka Otsuji*1*1Second Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health, School of Medicine*2NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION, Japan
8. The 29th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Electrocardiology, September 18-22, 2011Pitfall of Synthesized Posterior/Right-Sided Chest Lead Electrocardiograms.Yukio Saitoh*, Yoshinari Goseki*, YoshinaoYazaki*, Akira Yamashina** The Second Department of Internal Medicine, Tokyo Medical University, JapanP-Wave Dispersion in Synthesized 18-Lead ECG of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Patients.YasunoriHiranuma*, MarehikoUeda*, TakatsuguKajiyama*, NaotakaHashiguchi*, Tomonori Kanaeda*, Yusuke Kondo*, Masahiro Nakano*, Yoshio Kobayashi** Department of Cardiovascular Science and Medicine, Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
9. About the Normal Range in the Addition Leads(V3R,V4R,V5R, V7,V8,V9) When We Used Synthesized 18 Leads ECG.Jiro Suto*1, Tsuneo Takayanagi*1, Akira Yamashina*2*1Engineering Depertment1 Biomedical Instrument Technology Center NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION, Japan*2Cardiovascular Internal Medicine, Tokyo Medical University Hospital, Japan